Norwegian Municipal Finances Report
May 30, 2025
Executive Summary
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the current state of municipal finances in Norway, highlighting key trends, challenges, and future outlook. Norwegian municipalities face significant financial pressures due to demographic changes, increasing welfare obligations, and infrastructure needs. The operating margin has declined to 5.3% in 2023, while interest burden has increased to 3.9%. Demographic shifts, particularly population aging and urbanization, are creating disparities between municipalities. Recent policy developments, including administrative reforms and changes in tax distribution, aim to address these challenges but require careful implementation and monitoring.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Norwegian Municipal Finances
Norwegian municipalities play a crucial role in the country's governance structure, responsible for providing essential services such as primary education, healthcare, social services, and local infrastructure. The financial health of these municipalities is vital for ensuring quality public services and sustainable local development.
Norway's 356 municipalities (as of 2023) vary significantly in size, population, and financial capacity. Their primary funding sources include local taxes (approximately 55%) and government transfers (approximately 45%), with additional revenue from user charges and property management.
This report examines the current state of municipal finances in Norway, analyzing recent trends, identifying key challenges, and assessing future prospects. It draws on data from Statistics Norway (SSB), the Ministry of Local Government, and other official sources to provide a comprehensive overview of the financial landscape facing Norwegian municipalities.
2. Recent Trends in Income and Expenditure
Norwegian municipal finances have undergone significant changes in recent years, with several notable trends emerging in both income sources and expenditure patterns.
Income Trends
Municipal income in Norway comes primarily from two sources: local taxes (55%) and government transfers (45%). The tax revenue includes income tax, wealth tax, and property tax, while government transfers are designed to equalize differences between municipalities and ensure adequate service provision across the country.
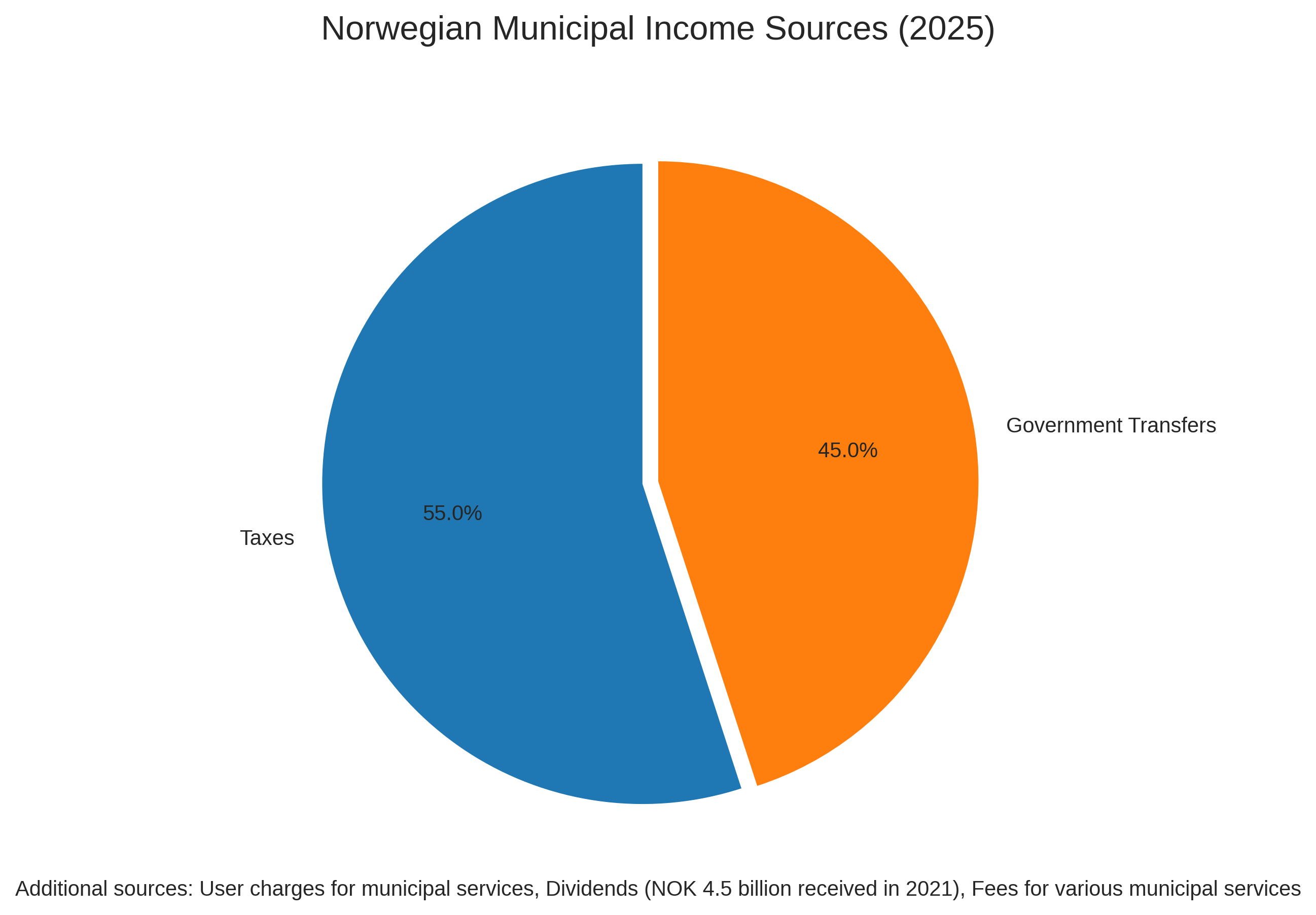
As shown in the chart above, there have been fluctuations in municipal income sources over recent years. The financial indicators reveal that:
- The operating margin has declined to 5.3% in 2023, indicating reduced financial flexibility
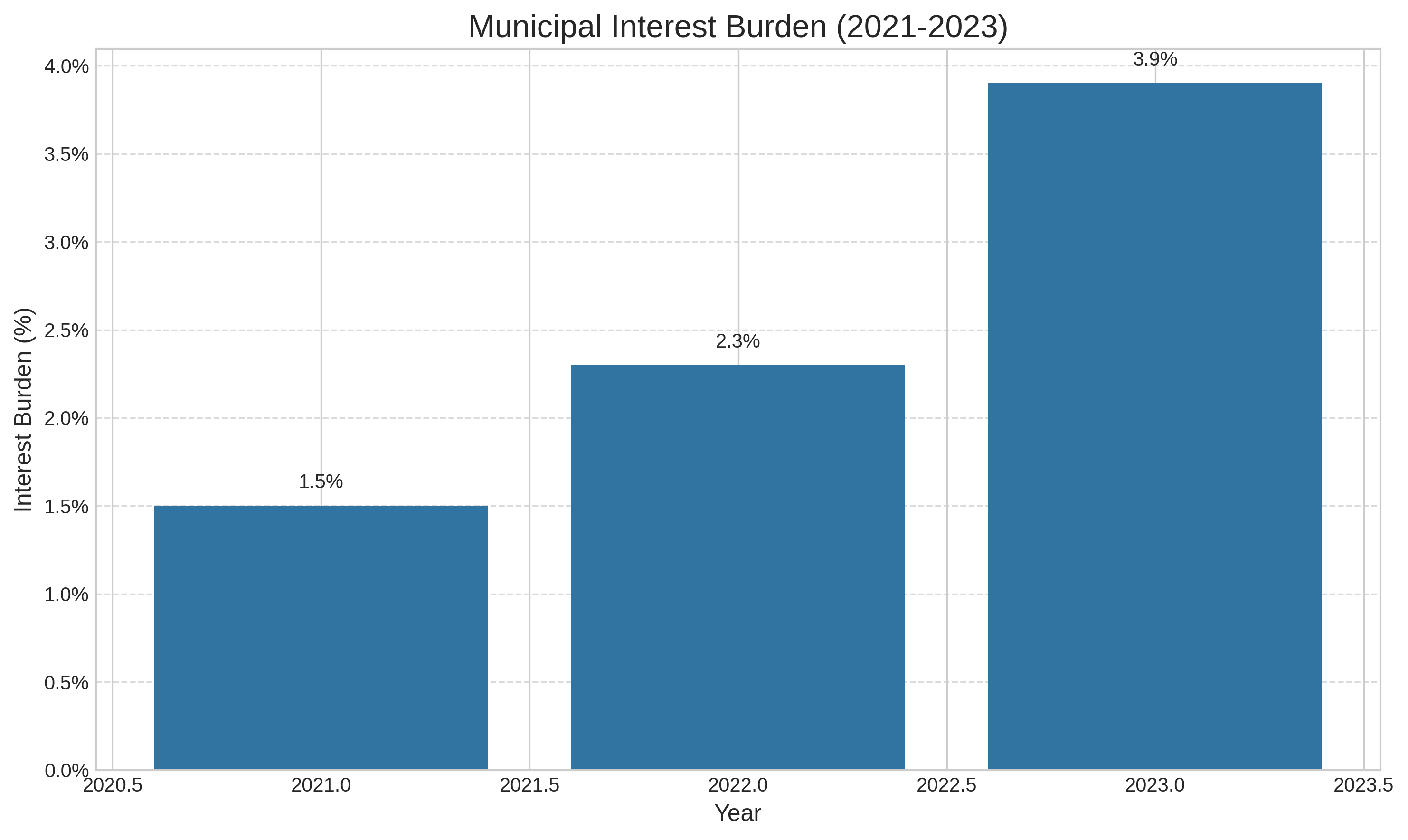
- Interest burden has increased to 3.9% in 2023, up from 1.5% in 2021, reflecting higher borrowing costs
- Net financial liabilities have grown by 8.2% since 2021
Expenditure Trends
Municipal expenditures have been rising steadily, driven by increasing service demands, particularly in healthcare and elderly care. The expenditure patterns reflect the growing responsibilities placed on municipalities.
Key expenditure challenges include:
- Rising operational costs, particularly in labor-intensive sectors
- Increasing infrastructure maintenance requirements
- Growing demand for specialized services
| Indicator | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interest Burden | 1.5% | 2.3% | 3.9% | Increasing |
| Operating Margin | N/A | N/A | 5.3% | Declining |
| Free Equity Operational Account | N/A | 14.7% | 13.2% | Declining |
| Gross Investment Expenditures | N/A | 14.9% | 15.1% | Stable |
3. Key Challenges Municipalities Are Facing
3.1 Demographic Changes
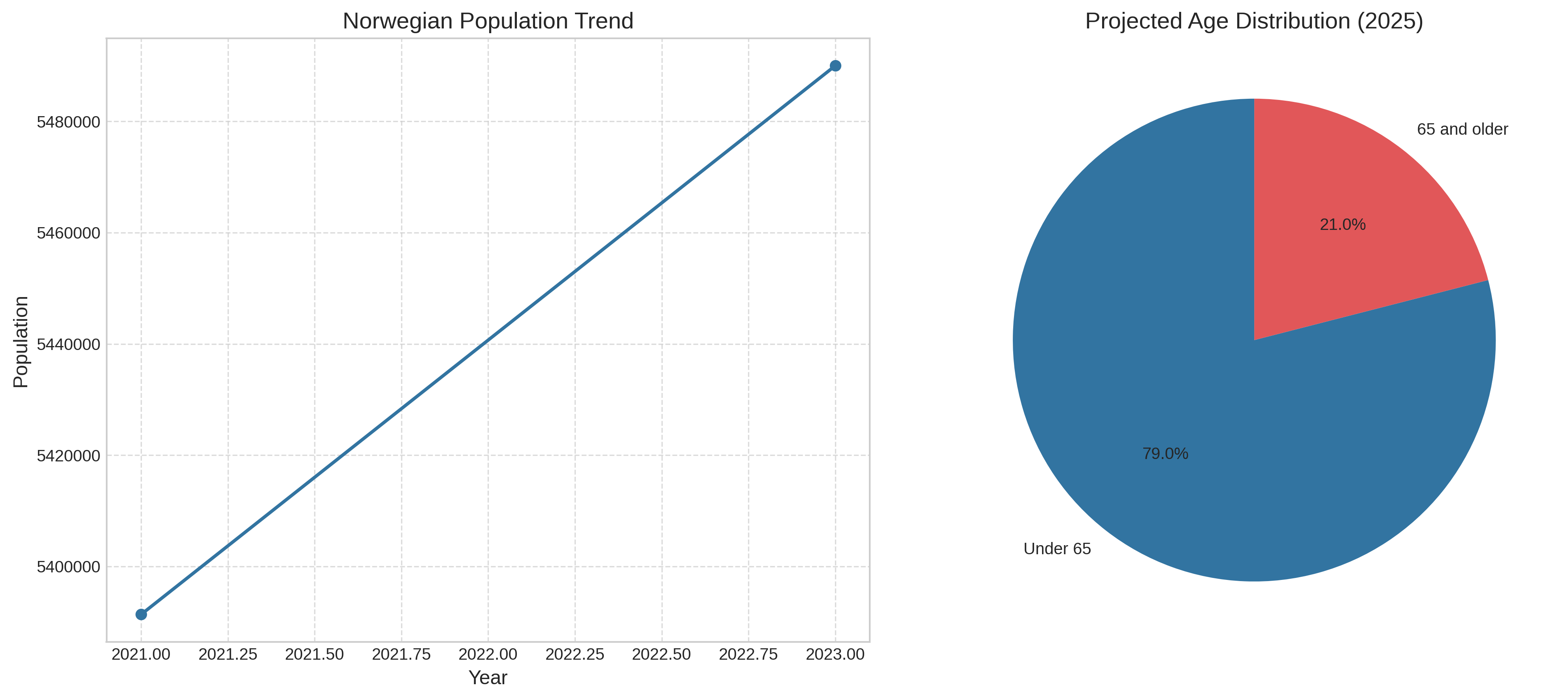
Demographic shifts represent one of the most significant challenges for Norwegian municipalities. The population is aging rapidly, with the percentage of residents aged 67 and above increasing from 16% in 2021 to 17.2% in 2023. Simultaneously, urbanization continues as people move from rural to urban areas.
These demographic trends create several challenges:
- Rural municipalities face declining populations and tax bases
- Urban municipalities struggle with rapid growth and infrastructure demands
- The aging population increases demand for healthcare and elderly services
- Workforce shortages in key service sectors
| Indicator | Value | Impact on Municipal Finances |
|---|---|---|
| Total Population (2023) | 5,490,000 | Base for tax revenue and service demand |
| Population Growth | Consistent growth | Increased demand for services |
| Population Density | 15 people per km² | Challenges in service delivery efficiency |
| Percentage 65 and older | 21% | Higher healthcare and elderly care costs |
3.2 Welfare Obligations
Norwegian municipalities bear significant welfare responsibilities, including:
- Primary healthcare services
- Elderly care and nursing homes
- Primary and lower secondary education
- Social services and child welfare
These obligations are becoming increasingly costly due to:
- Rising standards and expectations for service quality
- Growing number of elderly requiring care
- Increasing complexity of health and social needs
- Labor shortages in healthcare and education sectors
The financial pressure is particularly acute in smaller municipalities with limited resources and declining populations. According to the data, municipalities spend approximately 80% of their budgets on welfare services, with healthcare and elderly care representing the fastest-growing expenditure categories.
3.3 Infrastructure Needs
Norwegian municipalities face substantial infrastructure challenges, including:
- Aging water and sewage systems requiring renovation
- Road maintenance and transportation infrastructure
- Public buildings (schools, healthcare facilities, administrative buildings)
- Digital infrastructure and technological modernization
The estimated maintenance backlog for municipal infrastructure exceeds 300 billion NOK nationwide. This creates a significant financial burden, particularly as interest rates have risen, increasing the cost of borrowing for infrastructure investments.
Regional disparities are evident, with some municipalities having significantly better infrastructure than others. Urban municipalities face capacity challenges due to population growth, while rural municipalities struggle with maintaining extensive infrastructure with a smaller tax base.
4. Relevant National Policy Developments
Several recent policy developments have significant implications for municipal finances in Norway:
Administrative Reforms
The regional reform initiated in 2020 has been partially reversed, creating uncertainty for municipal planning and finances. The reform aimed to create larger, more efficient administrative units but faced political resistance and implementation challenges.
Tax Distribution Changes
Recent changes to the tax distribution system include:
- Municipal tax rate: 0.7%
- National tax rate: 0.4%
- Property tax: Municipal option with maximum rate of 0.7%
These changes aim to provide municipalities with more stable revenue sources but have been criticized for not adequately addressing regional disparities.
COVID-19 Impact Measures
The government implemented several measures to support municipalities during the COVID-19 pandemic, including:
- Government guarantees amounting to 100 billion kroner
- Direct financial support for increased healthcare costs
- Compensation for lost tax revenue
While these measures helped municipalities weather the immediate crisis, the long-term fiscal impact remains a concern as support programs are phased out.
Nordic Comparison
Norway's approach to municipal finance differs somewhat from its Nordic neighbors:
- Tax-to-GDP ratios (2021): Denmark 46.9%, Norway 42.2%, Sweden 42.6%
- Norway has a higher degree of central government transfers compared to Sweden
- Denmark has more extensive municipal taxation powers
These differences reflect varying approaches to fiscal decentralization and local autonomy within the Nordic model.
5. Forward-looking Assessment of Risks and Opportunities
Key Risks
- Demographic Pressures: Norway is projected to become a "super-aged society" with over 21% of the population aged 65+ by 2030, increasing demand for elderly care services.
- Rising Interest Rates: Higher borrowing costs affect municipal investment capacity and debt servicing.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Municipalities face increasing costs for climate resilience measures and infrastructure adaptation.
- Regional Disparities: Growing differences between urban and rural municipalities threaten equal service provision.
- Labor Market Challenges: Shortages of qualified personnel in healthcare, education, and technical fields.
Opportunities
- Digitalization: Digital transformation offers potential efficiency gains in service delivery and administration.
- Inter-municipal Collaboration: Shared services and resources can improve efficiency without full municipal mergers.
- Green Transition: Investments in sustainable infrastructure can reduce long-term operational costs.
- Service Innovation: New models of service delivery can improve outcomes while controlling costs.
- Revenue Diversification: Exploring alternative funding sources beyond traditional taxation and transfers.
| Year | GDP Growth | Municipal Financial Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 0.5% | Limited revenue growth |
| 2024 | 1.2% | Modest improvement in fiscal capacity |
| 2025 | 2.1% | Potential for improved financial stability |
The future financial sustainability of Norwegian municipalities will depend on their ability to adapt to these challenges while leveraging opportunities for innovation and efficiency. National policies that support municipal adaptation and provide adequate funding will be crucial for maintaining Norway's high standards of local public services.
6. Conclusion
Norwegian municipal finances face significant challenges in the coming years, driven by demographic changes, increasing service demands, and infrastructure needs. The declining operating margins and increasing interest burden observed in recent years indicate growing financial pressure that requires strategic responses.
Key findings from this analysis include:
- Municipal operating margins have declined to 5.3% in 2023, limiting financial flexibility
- Interest burden has more than doubled since 2021, reaching 3.9% in 2023
- Demographic shifts, particularly population aging and urbanization, are creating significant disparities between municipalities
- Infrastructure maintenance backlogs exceed 300 billion NOK nationwide
- Recent policy reforms have created both challenges and opportunities for municipal finances
To ensure sustainable municipal finances in the future, a combination of approaches will be necessary:
- Structural reforms that balance efficiency with local democracy
- Innovative service delivery models that maintain quality while controlling costs
- Strategic infrastructure investments that reduce long-term operational expenses
- Fiscal policies that provide adequate and predictable funding for municipal responsibilities
- Enhanced inter-municipal collaboration to achieve economies of scale
The financial health of Norwegian municipalities is essential for maintaining the country's high standards of public services and quality of life. Addressing the challenges identified in this report will require coordinated efforts from all levels of government, as well as innovative approaches to service delivery and resource management.
7. References and Citations
- Statistics Norway (SSB). (2023). Municipal finances statistics 2023.
- Ministry of Local Government and Regional Development. (2023). White paper on municipal structure and finances.
- Norwegian Association of Local and Regional Authorities (KS). (2023). Annual report on municipal economic outlook.
- OECD. (2023). Economic Survey of Norway 2023.
- Statistics Norway (SSB). (2023). Population projections 2023-2050.
- Ministry of Finance. (2023). National Budget 2024: Municipal finance chapter.
- Norwegian Institute for Urban and Regional Research. (2022). Report on urbanization trends in Norway.
- Norwegian Advisory Commission on Local Government Finances. (2023). Annual recommendations.